
Back فاموتيدين Arabic فاموتیدین AZB ফ্যামোটিডিন Bengali/Bangla Ffamotidin Welsh Famotidin German Φαμοτιδίνη Greek Famotidina Spanish فاموتیدین Persian Famotidine French Famotidin Croatian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /fəˈmɒtɪdiːn/ |
| Trade names | Pepcid, Zantac 360, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a687011 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| Drug class | Histamine H2 receptor antagonist |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 40–45% (by mouth)[2] |
| Protein binding | 15–20%[2] |
| Onset of action | 90 minutes |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5–3.5 hours[2] |
| Duration of action | 9 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (25–30% unchanged [Oral])[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.116.793 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
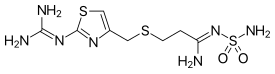
| Formula | C8H15N7O2S3 |
| Molar mass | 337.44 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Famotidine, sold under the brand name Pepcid among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist medication that decreases stomach acid production.[4] It is used to treat peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.[4] It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.[4] It begins working within an hour.[4]
Common side effects include headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, and dizziness.[4] Serious side effects may include pneumonia and seizures.[4][5] Use in pregnancy appears safe but has not been well studied, while use during breastfeeding is not recommended.[1]
Famotidine was patented in 1979 and came into medical use in 1985.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[5] In 2022, it was the 49th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 13 million prescriptions.[7][8]
- ^ a b "Famotidine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 16 December 2023. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ a b c d e "Famotidine tablet". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 31 March 2024. Retrieved 6 March 2021.
- ^ "Zantac 360- famotidine tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 17 May 2022. Archived from the original on 6 July 2022. Retrieved 6 July 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f "Famotidine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 74–75. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 444. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Famotidine Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 30 August 2024.